概述
在实际的生产中,我们经常会遇到id生成问题。通常,我们对id生成现象都有一个最基础的要求保证id的唯一性。针对这个最基础要求,经常用到的解决方案有以下几种。
- 微软公司通用唯一识别码(UUID)
- Twitter公司雪花算法(SnowFlake)
- 基于数据库的id自增
- 对id进行缓存
其中,使用数据库进行id自增是在单机应用中使用最普遍的id生成方式,它能够完全保证id的不重复。但id的自增并不是在任何数据库都支持,这就给数据库迁移造成了麻烦。并且,数据库的解决方案在分布式环境下的只能保证单个数据库作为生成数据库,存在单点故障的危险。
而微软的UUID显然是一种极佳的解决方案,它由当前日期时间、时钟序列、全局唯一的机器标识号来生成一段无序的字符串id。它不仅能理论上实现id的不重复(实际id可能重复,但几率极小)。但问题又来了,我们前面说到它的id是无序的。虽然它满足了我们的基础要求,但实际很多的生产中我们还有id根据时间进行递增的进阶要求。这显然是无法实现的。
所以,在本章我们讲一下Twitter公司的雪花算法是如何进行id生成的。
雪花的结构
首先,我们从它的设计入手,自己想一下,如果让我们设计一个id,如何保证既能唯一又能按照时间递增?
首先,既然要按照时间递增,那么这个id一定是个数,而不是字符串。并且在id中时间要作为第一影响因素,越晚生成的id,数字越大。那么整个数字id的前几位一定是时间戳。这就实现了按照时间递增。
那么同时间的并发生成如何保证唯一性呢?我们还会想到在分布式情况下要在多台机器上生成id,那么直接再加上这台机器的id就好了。
Ok,继续思考,时间相同,在同一台机器上生成的多个id如何保证唯一性,这时候就会向,也许可以再在后面加一串随机数或者序列之类的。
想到这,就有了下面的雪花算法的结构图。
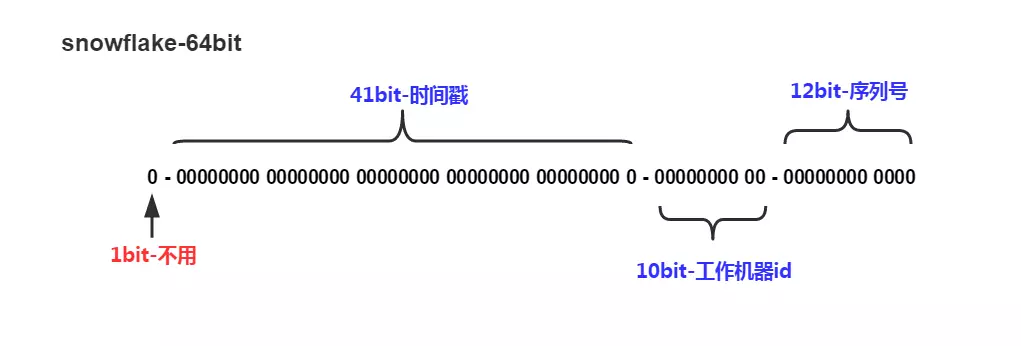
- 整个结构是64位,所以我们在Java中可以使用long来进行存储。
- 1 bit是符号位,丢弃不用。
- 41 bits时间戳,可表示最大$$(2^{41}-1) / (1000 60 60 24 365) = 69$$,即可保证约69年内的id不重复。
- 10 bits的机器id,5 bits作为
datacenterId,5 bits作为workerId。 - 12 bits的序列号,用来标识同一时间同一台机器生成的id,$$2^{12}-1 = 4095$$,即允许同一时间同台机器生成4095个id。
可以看出,雪花算法生成的id既保证了唯一性,又因为是long存储,所以能够按照时间进行排序。至于69年的限制。。。。。。反正69年后公司在不在都不一定了,关我啥事。
代码实现
twitter原厂生产的实现代码是用scala写的,发布在twitter的git仓库中。
/** Copyright 2010-2012 Twitter, Inc.*/
package com.twitter.service.snowflake
import com.twitter.ostrich.stats.Stats
import com.twitter.service.snowflake.gen._
import java.util.Random
import com.twitter.logging.Logger
/**
* An object that generates IDs.
* This is broken into a separate class in case
* we ever want to support multiple worker threads
* per process
*/
class IdWorker(val workerId: Long, val datacenterId: Long, private val reporter: Reporter, var sequence: Long = 0L)
extends Snowflake.Iface {
private[this] def genCounter(agent: String) = {
Stats.incr("ids_generated")
Stats.incr("ids_generated_%s".format(agent))
}
private[this] val exceptionCounter = Stats.getCounter("exceptions")
private[this] val log = Logger.get
private[this] val rand = new Random
val twepoch = 1288834974657L
private[this] val workerIdBits = 5L
private[this] val datacenterIdBits = 5L
private[this] val maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits)
private[this] val maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits)
private[this] val sequenceBits = 12L
private[this] val workerIdShift = sequenceBits
private[this] val datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits
private[this] val timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits
private[this] val sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits)
private[this] var lastTimestamp = -1L
// sanity check for workerId
if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0".format(maxWorkerId))
}
if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0".format(maxDatacenterId))
}
log.info("worker starting. timestamp left shift %d, datacenter id bits %d, worker id bits %d, sequence bits %d, workerid %d",
timestampLeftShift, datacenterIdBits, workerIdBits, sequenceBits, workerId)
def get_id(useragent: String): Long = {
if (!validUseragent(useragent)) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1)
throw new InvalidUserAgentError
}
val id = nextId()
genCounter(useragent)
reporter.report(new AuditLogEntry(id, useragent, rand.nextLong))
id
}
def get_worker_id(): Long = workerId
def get_datacenter_id(): Long = datacenterId
def get_timestamp() = System.currentTimeMillis
protected[snowflake] def nextId(): Long = synchronized {
var timestamp = timeGen()
if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {
exceptionCounter.incr(1)
log.error("clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests until %d.", lastTimestamp);
throw new InvalidSystemClock("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds".format(
lastTimestamp - timestamp))
}
if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask
if (sequence == 0) {
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp)
}
} else {
sequence = 0
}
lastTimestamp = timestamp
((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) |
(datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) |
(workerId << workerIdShift) |
sequence
}
protected def tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp: Long): Long = {
var timestamp = timeGen()
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = timeGen()
}
timestamp
}
protected def timeGen(): Long = System.currentTimeMillis()
val AgentParser = """([a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z\-0-9]*)""".r
def validUseragent(useragent: String): Boolean = useragent match {
case AgentParser(_) => true
case _ => false
}
}
翻译为Java代码如下(代码来自理解分布式id生成算法SnowFlake)
public class IdWorker{
private long workerId;
private long datacenterId;
private long sequence;
public IdWorker(long workerId, long datacenterId, long sequence){
// sanity check for workerId
if (workerId > maxWorkerId || workerId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("worker Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0",maxWorkerId));
}
if (datacenterId > maxDatacenterId || datacenterId < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("datacenter Id can't be greater than %d or less than 0",maxDatacenterId));
}
System.out.printf("worker starting. timestamp left shift %d, datacenter id bits %d, worker id bits %d, sequence bits %d, workerid %d",
timestampLeftShift, datacenterIdBits, workerIdBits, sequenceBits, workerId);
this.workerId = workerId;
this.datacenterId = datacenterId;
this.sequence = sequence;
}
private long twepoch = 1288834974657L;
private long workerIdBits = 5L;
private long datacenterIdBits = 5L;
private long maxWorkerId = -1L ^ (-1L << workerIdBits);
private long maxDatacenterId = -1L ^ (-1L << datacenterIdBits);
private long sequenceBits = 12L;
private long workerIdShift = sequenceBits;
private long datacenterIdShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits;
private long timestampLeftShift = sequenceBits + workerIdBits + datacenterIdBits;
private long sequenceMask = -1L ^ (-1L << sequenceBits);
private long lastTimestamp = -1L;
public long getWorkerId(){
return workerId;
}
public long getDatacenterId(){
return datacenterId;
}
public long getTimestamp(){
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public synchronized long nextId() {
long timestamp = timeGen();
if (timestamp < lastTimestamp) {
System.err.printf("clock is moving backwards. Rejecting requests until %d.", lastTimestamp);
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("Clock moved backwards. Refusing to generate id for %d milliseconds",
lastTimestamp - timestamp));
}
if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
if (sequence == 0) {
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);
}
} else {
sequence = 0;
}
lastTimestamp = timestamp;
return ((timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift) |
(datacenterId << datacenterIdShift) |
(workerId << workerIdShift) |
sequence;
}
private long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp) {
long timestamp = timeGen();
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = timeGen();
}
return timestamp;
}
private long timeGen(){
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
//---------------测试---------------
public static void main(String[] args) {
IdWorker worker = new IdWorker(1,1,1);
for (int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
System.out.println(worker.nextId());
}
}
}
代码阅读
仔细看整个代码的话,阅读起来也并不困难。首先,这些代码是运行在每台机器上的,所以datacenterId与workderId作为参数传入,我们需要解决的只是时间戳和序列的生成。
首先是时间戳的生成,时间戳生成十分简单,就是单纯取当前的系统时间
private long timeGen(){
return System.currentTimeMillis();
}
在最后组合成id时,先执行timestamp - twepoch,twepoch变量是我们定义的起始的时间戳,这样可以让时间戳存储时间更久。然后再执行(timestamp - twepoch) << timestampLeftShift进行移位。这样就取到了41位的时间戳。
然后就是序列,序列的生成直接就按照顺序递增。最初序列变量sequence为0。当新生成的id与上一个id的时间戳相同时,则直接让序列加一。
if (lastTimestamp == timestamp) {
sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;
if (sequence == 0) {
timestamp = tilNextMillis(lastTimestamp);
}
} else {
sequence = 0;
}
这里要注意一点,因为序列是12 bits长度,所以当超出长度时,执行完sequence = (sequence + 1) & sequenceMask;之后,得到的sequence为0。所以这时候进入一个循环等待一直等到时间戳变化再进行本次的id生成。
private long tilNextMillis(long lastTimestamp) {
long timestamp = timeGen();
while (timestamp <= lastTimestamp) {
timestamp = timeGen();
}
return timestamp;
}



